Innovative approach to construction material recycling
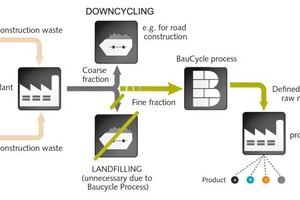
In Germany, about 5 million t of fine-grained building rubble are generated each year. This fine fraction has gone to landfills so far and is partly re-used as subgrade in the field of road and dump construction. To enable the recovery of the valuable raw materials used in concrete, such as sand or gravel, and to reintroduce them in the production cycle, the four Fraunhofer Institutes have set themselves the target of realizing an innovative recycling process of fine-grained demolition rubble. For this purpose, the project “BauCycle” was initiated, in the context of which researchers address the entire value added chain - from innovative optical sorting processes and logistics networks up to the development of high-quality construction material. This kind of recycling of demolition rubble aims to sustainably protect primary raw materials and counteract a shortage of land for landfills.
The construction industry in one of the most resource-intensive economic sectors in Germany. 600 million t of construction minerals are used each year. With approx. 100 billion t, the national total portfolio of buildings has become a significant raw materials stock. By means of systematic recycling its components could be channeled back to the materials cycle after the end of use. The Fraunhofer in-house research project “BauCycle” has set itself the goal to develop new and economically attractive utilization options for the fine fractions (< 2 mm) of mineral construction waste which today is not yet reusable. Due to the heterogeneity of the materials and the technical and safety-related challenges of this mass flow, processing techniques, logistics concepts and product innovations are required that go far beyond the current technological level.
BauCycle supports the Fraunhofer strategies called “Producing in Cycles” and “Energy and Resource Efficiency” with the aim of generating valuable materials from today’s “problematic fraction”. With the planned new framework ordinance of the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety (BMUB), which aims at regulating the use of mineral replacement construction materials in technical buildings, the project is becoming increasingly topical. According to this ordinance, the application of the materials used so far in road and landfill construction is no longer allowed. This raises the need for new recycling routes.
Four Fraunhofer Institutes aiming at a comprehensive approach
The Fraunhofer Institutes for Building Physics IBP, for Material Flow and Logistics IML, for Optronics, System Technologies and Image Exploitation IOSB and for Environmental, Safety and Energy Technology UMSICHT pool their competences to develop a holistic technological and logistics solution for the circular economy in the building industry. For this purpose, a highly qualified team of researchers works on a novel opto-pneumatic sorting process for fine fractions, which is able to detect chemical differences in particles besides colors and brightness. Thus, rubble-relevant attributes, such as “sulphatic” or “siliceous” can be recorded and sorted according to these criteria. The optimum sorting result leads to the selective separation of gypsum particles from the construction waste. The gypsum content represents a decisive criterion for the recyclability of the concrete fraction.
For the fractions obtained through sorting, different approaches for the production of components will be elaborated in order to illustrate possible recycling routes and utilization potentials and to prove technical feasibility. Besides the utilization as cement raw material, also granulates for the use in acoustically active components shall be produced. The latter are components which, due to their micro and macro structure, are able to absorb sound and thus can be used in the field of noise protection. The future market for recycling materials and components is huge: porous mineral plates, for example, are predestined for the use as sound absorbers in noise protection walls and components. In 2013, noise protection walls with a size of 117 000 m2 were built on roadsides and about 62 km alongside rails. Furthermore, scientists are working on the development of cement-free bonding agents as an alternative to the conventionally used materials.
Since the product value added chains resulting from the BauCycle processes differ considerably from the models available in the building sector so far, they are accompanied by the development of a dynamic market platform. Similar to a commodities exchange that collects the offers of recycling companies and the demands of the recycling material processing companies, it supports the market launch of the products. Thus, BauCycle combines the three business areas of “Product Development”, “Sorting Technology” and “Marketing”.
Cross-Industry Marketing
As soon as the solution for fine-grained material from the building sector is available, it can be transferred to similar fractions in other branches of industry. Fine fractions occur in nearly all mechanical processing plants, for example in glass recycling, the mining industry, as residues from thermal processes of iron smelting or as foundry residues. Thus, processing, sorting and utilization of fine materials provides these three identified business fields with a potential that has not been tapped so far.